What is the standard for Venturi tube?
What is the standard for Venturi tube?
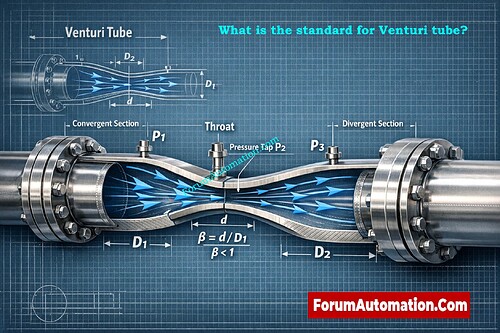
ISO 5167 and ASME MFC set standards for venturi tubes, including the geometry, discharge coefficient, installation, and precision needed for reliable flow monitoring.
International metrology standards mostly dictate how a Venturi tube (classical Venturi flowmeter) is shaped, installed, and how to find the discharge coefficient. These are the two most important things that affect accuracy and repeatability. ISO 5167 is the global standard. Parts 1 and 4 cover orifice, Venturi, and cone meters, and part 4 specifically covers classical Venturi tubes. It sets the geometric profiles (convergent angle, throat length, divergence), the allowable Reynolds ranges, the tapping locations, and the methods for calculating uncertainty used to figure out flowrate. Many manufacturers also adopt ASME MFC (for example, MFC-3M and MFC-8M), which makes Venturi manufacturing processes more consistent with the US market’s material and pressure classes and dimensional tolerances. In summary, design and make according to ISO 5167 (and ASME MFC instructions), calibrate the discharge coefficients, install the tapping and straight-run correctly, and expect some measurement uncertainty. When you send in engineering posts or spec sheets, make sure to include the standard (ISO 5167-4:2003), the manufacturer’s calibration certificate, and the recommended Reynolds-number band. These are the first three things that auditors, metrology laboratories, and EPCs ask for.
#Venturi flowmeasurement #ISO5167 #ASMEMFC instrumentation #ProcessEngineering