What is Resistor?
A resistor is an electrical component that prevents or regulates the flow of electric current in a circuit.
It turns electrical energy into heat & assists in voltage and current regulation.
The resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
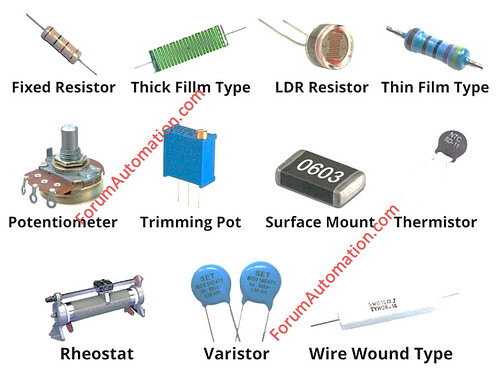
11 Different Types of Resistors
The different types of resistors are:
1). Fixed Resistor
2). Thick Film Resistors
3). LDR (light-dependent resistor)
4). Thin Film Resistors
5). Potentiometer
6). Trimming Pot (trimmer resistor)
7). Surface Mount Resistor (SMD)
8). Thermistor
9). Rheostat
10). Varistor
11). Wire Wound Resistors
1). Fixed Resistor
A fixed resistor’s resistance value is constant and cannot be modified. It is composed of carbon film, metal film (or) metal oxide.
Applications:
Voltage divider circuits
Current limiting
Biasing of transistor
Pull-up and pull-down resistors in digital circuits.
2). Thick Film Resistors
Thick Film Resistors created by placing a thick resistive layer upon a ceramic substrate. It is inexpensive and commonly used in conventional electronics.
Applications:
Consumer electronics
Power supplies
High-voltage circuits.
Automotive electronics
3). LDR (light-dependent resistor)
A resistor whose resistance varies with light intensity. Higher light equals lesser resistance.
Applications:
Automatic streetlights
Light-sensitive alarms.
Camera exposure schemes
Solar Garden Lights
4). Thin Film Resistors
Thin Film Resistors is created by placing a thin resistive film onto an insulating substrate. provides excellent accuracy, low tolerance & low noise.
Applications:
Precision analog circuits
measuring instruments
Medical devices
Aerospace and high frequency applications
5). Potentiometer
A variable resistor with three ends used to regulate voltage. Rotating the knob alters the resistance.
Applications:
Volume Controls
Speed control in fans.
Tunable power supplies
Calibration adjustments
6). Trimming Pot (trimmer resistor)
Trimming Pot (trimmer resistor) is a small preset variable resistor used to fine-tune circuits during calibration.
Applications:
Sensor calibration
Setting the reference voltage.
Tuning oscillators.
Adjusting gain in amplifiers
7). Surface Mount Resistor (SMD)
Surface Mount Resistor (SMD) is a small resistor utilized in surface-mount technology (SMT). Compact, lightweight, and ideal for automated PCB assembly.
Applications:
Mobile phones
Laptops
Embedded systems
High-density PCBs
8). Thermistor
Thermistor is a temperature-sensitive resistor. There are two types:
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient): Resistance reduces when temperature increases
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient): Resistance increases with temperature
Applications:
Temperature measurement
Thermal protection circuits
Inrush current limiting
HVAC systems
9). Rheostat
Rheostat is a high-power variable resistor utilized to manage current by manually altering the resistance.
Applications:
Laboratory testing
Dimming the lights
Controlling motor speed (in older systems)
Current adjustment in heaters
10). Varistor
Varistor is a voltage-dependent resistor whose resistance lowers dramatically when the voltage exceeds a certain threshold (surge protection).
Applications:
Surge protectors
Lightning arresters
Overvoltage protection in appliances.
SMPS protection
11). Wire Wound Resistors
Wire Wound Resistors is a resistor is manufactured by winding a resistive wire (often nichrome) around an insulating core. Highly accurate, powerful and stable.
Applications:
Power Equipment
Current sensing
High temperature surroundings
Industrial motor drives
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.