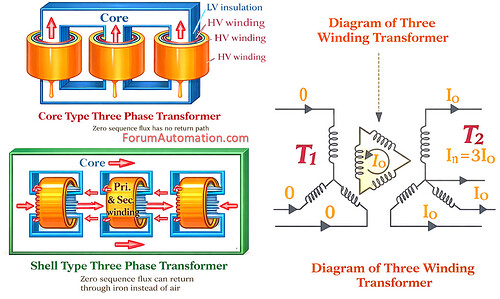
In the field of high-voltage engineering the primary and secondary windings frequently take position of importance.
However, the Tertiary Winding operates in the background to assure power system stability & reliability.
While the physical structure of Core-type & Shell-type transformers differs the primary engineering purpose remains the same:
1). Optimize flux management &
2). Control harmonics.
Why Tertiary Winding is used in Transformer?
The inclusion of a tertiary winding is frequently the key difference between a normal transformer and a high-performance system appropriate for complicated grids.
It has the following functions:
Harmonic Suppression
It creates a closed-loop path for third-harmonic current.
This stops voltage waveform distortion from damaging the main windings resulting in “clean” power supply.
Neutral Point Stabilization
In Star-Star (Y-Y) designs, the tertiary winding inhibits neutral shifting ensuring that the system remains balanced even under changing loads.
Auxiliary Power & Compensation
This power source is adaptable and can be used to power substation equipment or connect static capacitors for the reactive power compensation.
Fault Management
Controls imbalanced magnetic flux during ground faults improving transformer safety and protection.
The tertiary winding is a great example of how advanced engineering can frequently be found in components that are not visible. This “third player” improves a smart electrical design by handling the complicated processes of magnetic flux & stabilization.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.