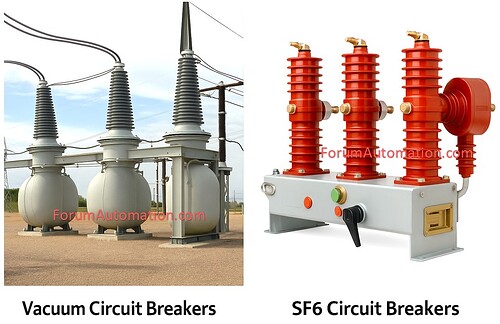
Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB)
VCBs utilize a vacuum medium to extinguish the arc.
They are commonly utilized in medium-voltage systems.
Suitable for applications up to 66 kV
Compact and low-maintenance
Excellent arc interruption performance at modest voltages.
However as the voltage rises so does the gap required for insulation making VCBs large and unsuitable for high voltage applications.
SF6 Gas Circuit Breakers
SF6 circuit breakers utilize Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6) gas which has exceptional:
Dielectric strength (2.5 times higher than air)
Arc-quenching capabilities
Suitable for high fault levels.
These characteristics make SF6 breakers the ideal choice for high-voltage & extra-high-voltage applications in the transmission networks.
Suitable for applications or range from 132 kV to 765 kV & higher.
More compact for the same rating.
Improved for rapid & repeated operations.
Reliable interruption at harsh conditions.
One disadvantage is that SF6 handling necessitates the deployment of leak detection systems because SF6 is a powerful greenhouse gas.
Difference Between VCB and SF6
VCB vs. SF6
| Parameter | VCB | SF6 Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Interrupting Medium | Vacuum | SF6 Gas |
| Voltage Range | Up to 66 kV | 132 kV and above |
| Size at High Voltage | Large / bulky | Compact |
| Arc Quenching | Good | Excellent |
| Dielectric Strength | Good | Very High |
| Maintenance | Low | Requires gas monitoring |
| Environmental Impact | Safe | Higher (SF6 GHG concerns) |
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.