Transformer impedance commonly represented as a percentage is an important factor in defining a transformer’s size, rating and performance.
Impedance is the opposition a transformer provides to the flow of current under short-circuit conditions and it is affected by both
- Winding resistance and
- Leakage reactance.
A greater impedance limits the short-circuit current protecting downstream equipment but it also results in some voltage drop under full load which must be taken into account when sizing the transformer.
When selecting a transformer the impedance value affects the current rating necessary to provide a specific load.
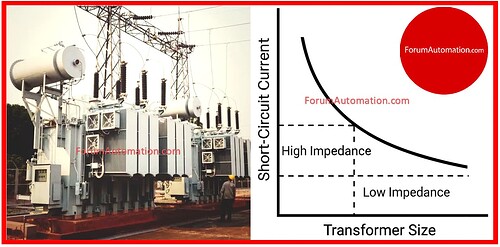
For the same load, a transformer with a higher impedance will have lower short-circuit currents which is potentially reducing mechanical stress on windings and fault damage.
A transformer with very low impedance, on the other end, allows for higher short-circuit currents requiring stronger construction and possibly a larger core & windings to effectively manage fault currents.
Furthermore, transformer impedance effects voltage regulation.
A transformer with a low impedance produces voltage closer to nominal under full load but it may require a bigger size to securely manage short-circuit conditions.
High-impedance transformers may be smaller & less expensive but they have a higher voltage drop when loaded.
As a result, while designing (or) selecting a transformer engineers have to consider
- Impedance,
- Transformer size,
- Voltage control and
- Fault current capabilities
to assure the transformer’s and the linked system’s reliability, efficiency, and protection.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.