What is the range of LiDAR vs radar?
What is the Range of LiDAR vs Radar?
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging) are two common types of sensors. However, they work in quite different ways since they use different types of waves. For things like self-driving cars, industrial automation, surveying, military, and weather monitoring, it’s important to know how far LiDAR and radar can see.
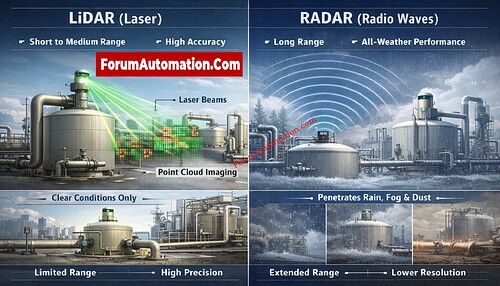
LiDAR systems employ laser light, usually infrared, to figure out how far away something is by measuring how long it takes for a light pulse to come back after hitting something. LiDAR range usually ranges from 50 to 300 meters in most industrial and automotive settings. Long-range, high-power LiDAR used for aerial mapping and defense can go as far as 2 to 5 kilometers in perfect weather. Fog, rain, dust, and intense sunshine can all have a big effect on LiDAR effectiveness since they scatter or absorb laser beams and make the range less effective.
Radio waves, which have significantly longer wavelengths, are used by radar systems. Radar can detect things far farther away than light can because radio waves can get through fog, rain, snow, and dust much better. Short-range radar systems work between 30 and 200 meters and are often used in cars to avoid collisions. Long-range radar can see things from several kilometers to hundreds of kilometers away. It is employed in aviation, weather monitoring, and military surveillance.
In short, LiDAR is great for 3D mapping and object categorization since it works better at shorter ranges and gives more accurate results. Radar is better at detecting things from a long distance and in all kinds of weather, which makes it more reliable in tough situations. Many modern systems use both technologies to get the best of both worlds.