What is the full meaning of SIS?
What is the full meaning of SIS?
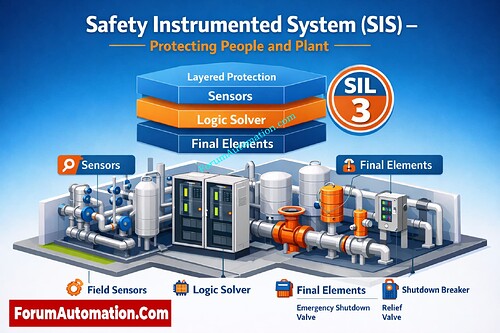
SIS is short for Safety Instrumented System. An SIS is a special set of sensors, logic, and final parts that are used in process industries and places with a lot of automation. They are designed to find dangerous situations and automatically bring the process to a safe state. A typical SIS has field sensors (for pressure, temperature, level, and flow), a safety logic solver (a safety PLC or a redundant logic solver), and final elements such emergency shutdown valves, relief devices, or shutdown breakers.
The main purpose of a SIS is to lower risk. It stops accidents from happening or lessens their effects when standard controls fail. Safety Integrity Level (SIL) is a key concept because it measures how reliable something needs to be.
The functional safety lifecycle covers design, commissioning, and maintenance. Standards like IEC 61508 and IEC 61511 guide SIS engineering for measurable safety performance. To avoid common cause failures, a good SIS should not depend on basic process control systems (BPCS).
It should also be checked routinely with proof tests and diagnostics to keep its SIL aim. For others who frequent the thread, add useful categories and phrases like “safety instrumented system definition,” “SIL proof test,” “IEC 61511,” “emergency shutdown,” and “layers of protection.” Short case studies, like an emergency shutdown on high level or pressure runaway, assist people understand how a SIS works as the last line of defence in a “layer of protection analysis” (LOPA). Always keep in mind that a SIS is not a fix for bad design. It is a planned safety layer that has been put in place and tested to lower risk to acceptable levels.