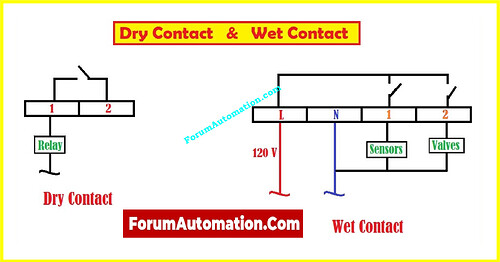
What is the difference between dry and wet contacts?
The words “wet” and “dry” connections refer to different kinds of electrical contacts dependent on whether they carry voltage or current.
Dry contacts, which are also called volt-free or potential-free contacts, don’t give off any power. They are just mechanical switches that turn on or off a circuit. When the contact closes, it makes a conduit for current to flow, but the voltage or current has to come from somewhere else. When electrical isolation is needed, dry contacts are typically utilized in relays, alarm systems, and signal interfaces. Because they don’t carry voltage, it’s safe to connect them to multiple systems without producing problems.
Wet contacts, on the other hand, are electrically active. These contacts get their voltage or current from the same place as the control system. When the contact is closed, it sends a live signal that can instantly turn on or off a device that is linked to it. Wet contacts are often found in PLC output modules or powered sensors. These are places where the control signal also has the power to move the system to the next stage.
The biggest difference is in the availability of power. You need an outside power source for dry contacts to work, whereas wet contacts already have electricity as part of the signal. This changes how they are connected and used in circuits.
If you measure across a closed dry contact, you won’t detect any voltage unless you connect an outside power source. When the contact is active, there will be voltage across a wet contact. When developing or fixing control systems, it’s important to know the difference because employing the improper sort of contact might cause parts to not communicate properly or possibly destroy the equipment.