What is Relay Testing? Why is it needed?
Relay testing is the systematic method of checking and verifying that a protective relay operates correctly under abnormal electrical conditions such as overcurrent, earth fault, overvoltage (or) short circuit.
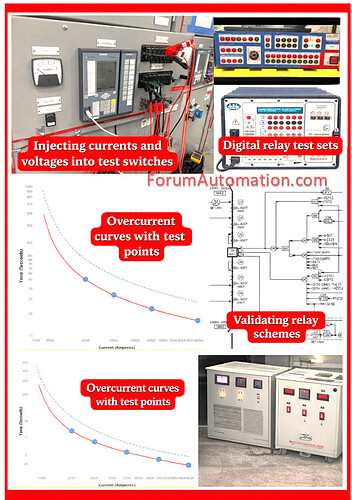
During relay testing fault conditions are simulated either by injecting current (or) voltage and the relays response: pickup value, operating time, logic and trip output is observed.
The primary purpose of relay testing is to ensure that the relay detects faults accurately and sends a correct tripping signal to the circuit breaker thereby isolating the faulty section of the power system.
Why Relay Testing is needed?
Relay testing is essential to ensure the safety, reliability and stability of electrical power systems.
Protective relays act as the first line of defense against electrical faults and any failure or incorrect operation can lead to severe equipment damage, fire hazards (or) complete system outages.
Testing confirms that relays function as intended and are ready to operate whenever a real fault occurs.
Correct Relay Operation
Relay testing verifies that the relay operates at the correct pickup current (or) voltage and within the specified time delay.
Over time, relay settings may drift due to aging, environmental conditions (or) internal component degradation.
Regular testing helps detect such issues early and ensures that the relay responds accuratey according to its design characteristics preventing delayed (or) failed tripping.
Protection of Electrical Equipment
One of the main reasons for relay testing is to protect expensive and important electrical equipment such as
Motors,
Generators,
Cables and
A properly tested relay quickly isolates faults before they escalate into major failures.
Without relay testing even a minor fault can cause overheating, insulation damage (or) catastrophic equipment failure resulting in high repair costs and long downtime.
Relay testing confirms that the relay settings are correctly programmed and properly coordinated with upstream and downstream protective devices.
Coordination ensures that only the nearest relay to the fault operates, while other relays remain unaffected.
This selective tripping minimizes power interruptions and maintains continuity of supply to healthy sections of the system.
Prevention of False or Nuisance Tripping
Incorrect (or) untested relays may trip unnecessarily during normal operating conditions leading to unwanted shutdowns and production losses.
Relay testing helps identify wiring errors, incorrect settings (or) internal malfunctions that could cause nuisance tripping.
By ensuring accurate operation testing improves system availability and operational confidence.
Importance in Commissioning and Maintenance
Relay testing is mandatory during new installation and commissioning of substations and electrical panels to confirm that the protection scheme is correctly implemented.
It is also a primary part of periodic preventive maintenance and must be performed after relay replacement, wiring modification (or) major fault events.
This ensures continued reliability throughout the equipment’s service life.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.