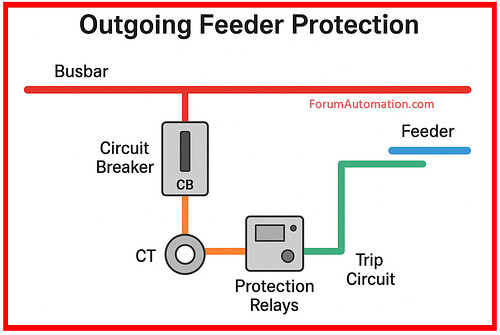
The term “outgoing feeder protection” describes the protections set in place for the circuits that leave a distribution board, switchgear or substation.
These feeders transmit electrical power from the busbars to various loads, including
- Distribution lines,
- Transformers,
- Motors and
- Other machinery.
Feeder protection’s fundamental objective is to promptly identify and isolate feeder faults (such as overload, short circuit, earth fault or overcurrent) to prevent equipment damage, disruption of other feeders’ supplies (or) dangerous conditions.
Purpose of Protecting Outgoing Feeders
Safety
Guards against risks brought on by electrical malfunctions for both people and equipment.
Quick Fault Isolation
Only the problematic feeder is disconnected, leaving the others operational.
System Stability
Prevents errors from spreading to the upstream system (grid, transformers, or busbars) in order to maintain system stability.
Protect Devices
Avoids insulation damage, overheating, and device failure from too much current.
Outgoing Feeder Protection Features
- When the current above predetermined thresholds (due to an overload or short circuit), the Overcurrent Protection (O/C) device trips.
- Earth Fault Protection (E/F) used to identifies fault currents or leaks that are going to the earth.
- Short Circuit Protection prevents harm by immediately clearing high fault currents.
- Optional Under/Over Voltage Protection use to trips when the voltage varies too much.
- In complicated networks, directional protection makes sure that only errors in the proper direction of power flow cause tripping.
Protective Equipment Used
- Circuit breakers are the primary protective switching device (ACB, MCCB, VCB, SF6 CB, etc.).
- Digital/microprocessor-based or electromechanical relays:
- OCR, or overcurrent relay
- EFR, or Earth Fault Relay
- Multiple-purpose numerical protection relays
- Current transformers, or CTs, are used to sense the relays’ current.
- Fuses quickly guard against short circuits in smaller feeds.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.