What is meant by Symmetrical Components?
Voltages and currents in a three-phase power system can become unbalanced as a result of faults, load imbalance (or) equipment failure. To analyze these conditions, 𝑺𝒚𝒎𝒎𝒆𝒕𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒂𝒍 𝒄𝒐𝒎𝒑𝒐𝒏𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒔 are utilized:
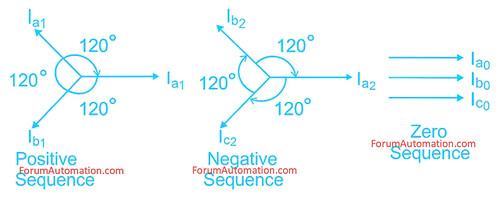
𝟏). 𝑷𝒐𝒔𝒊𝒕𝒊𝒗𝒆 𝑺𝒆𝒒𝒖𝒆𝒏𝒄𝒆
Three voltages or currents of equal amplitude.
They’re separated by 120°.
Rotate the same way as the original system.
Represents the electricity system’s regular operating condition.
𝑬x: A healthy system has a balanced positive sequence of phase voltages (Va, Vb, Vc).
𝟐). 𝑵𝒆𝒈𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒗𝒆 𝑺𝒆𝒒𝒖𝒆𝒏𝒄𝒆
Three voltages or currents of equal magnitude.
Separated by 120°, but spin in the opposite direction as the original arrangement.
Caused by imbalanced faults (such as line-to,line or unbalanced loads).
Harmful to motors & generators due to increased temperature.
𝑬x: A single-phase-to-ground fault causes negative sequence components.
𝟑). 𝒁𝒆𝒓𝒐 𝑺𝒆𝒒𝒖𝒆𝒏𝒄𝒆
Three voltages (or) currents have identical magnitude and phase (0° shift).
Typically connected with earth faults.
Exists when there is a return path (for example, through neutral/ground).
𝑬x: A single-line-to-ground fault in a system with a grounded neutral will result in high zero-sequence current.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.