IEEE 1584-2018 is the industry’s standard method used for calculating arc-flash hazards in electrical systems.
Although it provides detailed guidance and improves modeling accuracy, engineers should be aware of the following limitations:
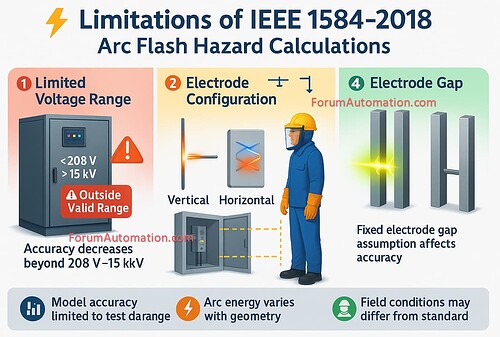
1). Limited Voltage Range
The standard is primarily intended for systems that operate between 208 V and 15 kV.
The calculation findings for systems outside of this voltage range such as very low-voltage DC or high-voltage transmission systems may be unreliable or not directly applicable.
2). Dependence on Electrode Configuration
Arc-flash results are largely dependent on electrode configuration (vertical, horizontal within box, etc.).
Because IEEE 1584-2018 contains empirical models for specified configurations, unlisted (or) non-standard combinations may produce less accurate or uncertain results.
3). Fixed Working Distance Assumption
The standard assumes a specific working distance (the distance across the worker’s body and the arc source).
Variations in working distance in real-world circumstances due to equipment size, maintenance position (or) operator habits that can have a substantial impact on incident energy statistics.
4). Electrode Gap Limitations
The computations in IEEE 1584-2018 use fixed electrode gap ranges determined from test data.
If the actual gap in equipment varies significantly, the model may fail to completely account for its effect on arc energy & propagation that is potentially impacting the results’ accuracy.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.