What are the different types of electromagnetic flow meters?
What Are the Different Types of Electromagnetic Flow Meters?
Using Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, electromagnetic flow meters (Mag meters) detect the flow rate of conductive liquids. When a conductive fluid moves through a magnetic field, it creates a voltage that is directly related to how fast it is moving. There are different varieties of electromagnetic flow meters, and they are accessible based on how they are made, how they are used, and how they are installed.
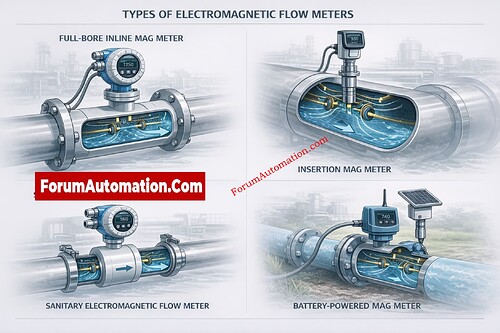
1. Full-Bore (Inline) Electromagnetic Flow Meters
This is the most prevalent kind. The meter body goes straight into the pipeline, and the flow tube is always full of liquid.
They are quite accurate (±0.2% to ±0.5%), work well over and over again, and are used a lot in water, wastewater, chemicals, slurry, and pulp and paper applications.
2. Insertion Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Insertion mag meters have a probe that goes into the pipe. This makes them good for big pipelines when full-bore meters would be too expensive.
They are often used for irrigation, cooling water, and raw water. They are not as accurate as inline meters.
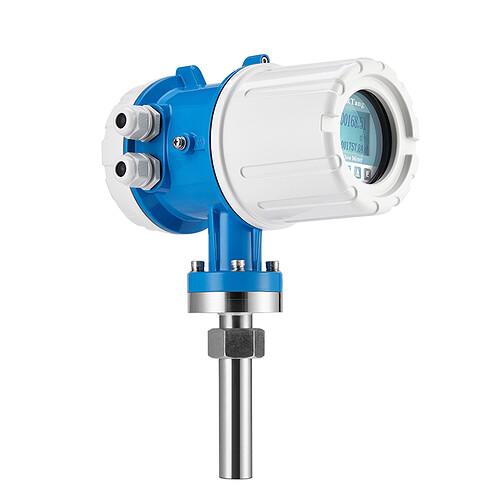
3. Low-Flow / Micro-Flow Electromagnetic Flow Meters
These meters are used in dosing systems, chemical injection, and batching applications. They are made for small pipes and very low flow rates.
They give steady measurements when regular mag meters don’t work.
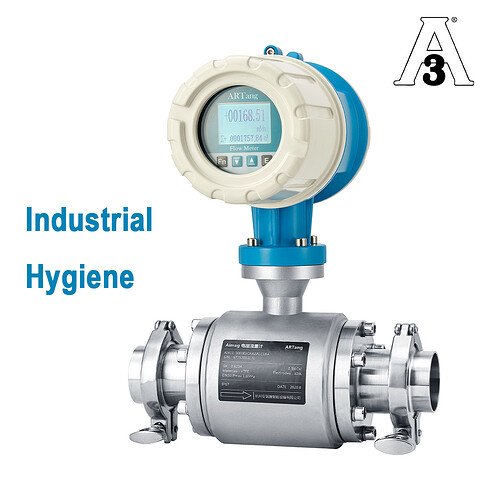
4. Sanitary (Hygienic) Electromagnetic Flow Meters
The liners, smooth surfaces, and clean connections on these meters are all safe for food.
They are used a lot in the pharmaceutical, food and drink, dairy, and biotech industries, and they meet CIP/SIP standards.
5. Battery-Powered and Remote Mag Meters
These meters run on batteries and send data wirelessly or on a regular basis. They are great for water distribution networks that are located far away or underground.
-
Full-Bore (Inline) Electromagnetic Flow Meters This is the most prevalent kind. The meter body goes straight into the pipeline, and the flow tube is always full of liquid. They are quite accurate (±0.2% to ±0.5%), work well over and over again, and are used a lot in water, wastewater, chemicals, slurry, and pulp and paper applications.
-
Insertion type Electromagnetic Flowmeter Insertion type electromagnetic flowmeter is a reliable measuring instrument for liquid flow measurement in large and medium caliber pipes (DN25-DN3000mm). Meet the needs of many different applications. Flow rate measurement range: 0.1m/s-15 m/s, protection grade: IP68, for pipeline electromagnetic flowmeter in the large pipeline installation difficulties, costs and other defects.
-
Sanitary Electromagnetic Flowmeter Sanitary electromagnetic flowmeter adopts a new type of sanitary lining materials and lining process, in line with the hygiene requirements of the food industry, while the use of stainless steel shell and stainless steel clamp connection, easy to electromagnetic flowmeter rapid disassembly, cleaning, so that the electromagnetic flowmeter is not easy to be contaminated in the process of use, and can effectively prevent the measurement of the fluid residue in the measurement pipe accumulation.
-
Battery-powered Electromagnetic Flow Meter A battery-powered electromagnetic flow meter is designed for applications where a power supply is unavailable or impractical. It operates using an internal battery, making it ideal for remote locations, temporary flow measurement, or areas with unreliable power sources.
-
Split-type Electromagnetic Flow Meter A split-type electromagnetic flow meter (also known as a remote-type electromagnetic flow meter) consists of two separate components: Sensor (Flow Tube) – Installed in the pipeline to measure flow. Transmitter (Converter) – Mounted separately, connected via a signal cable for data processing and display.