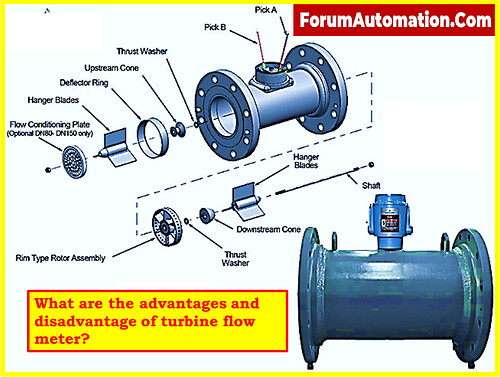
- Turbine flow meters are widely employed in a variety of industrial applications, including fuel gas distribution.
- When used in this environment, these devices have numerous advantages and drawbacks.
Advantages:
High Accuracy:
- Turbine flow meters give accurate measurements in the fuel gas industry.
- They can achieve great levels of precision, making them useful for applications requiring accurate flow rate measurements.
Wide Range of Flow Rates:
- Turbine flow meters are capable of measuring a wide range of flow rates, from low to high.
- Because of their versatility, they can be employed in a wide range of fuel gas applications, suiting both low and high-volume situations.
Responsive:
- Turbine flow meters are extremely responsive to variations in flow rates.
- They can detect flow changes fast, making them ideal for applications that require quick modifications in response to changing gas demand.
Low Pressure Drop:
- Because these meters have a low pressure drop, they do not considerably obstruct the passage of gas through the pipeline.
- This is critical in the fuel gas industry, where pressure control is critical.
Longevity:
- Turbine flow meters can have a lengthy service life if properly maintained.
- Because of their long-term durability and resilience to wear and tear, they are a cost-effective alternative for long-term use.
Digital Output:
- Many turbine flow meters have digital output options that allow them to readily connect with data gathering and control systems, making data logging and process control easier.
Disadvantages:
Contaminant Sensitivity:
- Turbine flow meters are susceptible to impurities in the gas stream, such as dirt or particle matter.
- This sensitivity might lead to decreased accuracy if the gas is not properly filtered and cleaned before entering the meter.
Risk of Damage:
- Turbine flow meters are ideally suited for detecting the flow of clean, low-viscosity gases.
- They might struggle with particularly viscous fuels or gasses of changing composition.
Calibration and Maintenance:
- To ensure accuracy, turbine flow meters require regular calibration and maintenance.
- This can increase the overall cost of ownership and could lead to meter downtime.
Expensive for Low Flow Rates:
- Turbine flow meters can be quite costly when used for very low flow rates. In such cases, alternative metering technologies may be more cost-effective.
Electromagnetic Interference:
- External electromagnetic interference can have an impact on the functioning of electronic components in turbine flow meters.
- To mitigate this problem, proper shielding and installation are required.
- Because of their excellent accuracy, wide flow rate range, and responsiveness, turbine flow meters are appropriate for many fuel gas service applications.
- They do, however, have drawbacks, such as sensitivity to pollutants, potential damage from pressure surges, and the need for regular maintenance.
- To achieve precise and reliable measurements, the metering technology selected should take into account the unique needs and conditions of the fuel gas service.