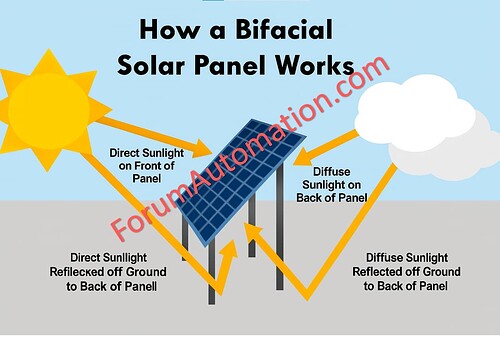
What are Bifacial Solar Panels?
Bifacial solar panels create power from both sides with the front capturing direct sunlight and the back collecting reflected light from ground (albedo effect).
This increases total energy yield by 5% to 30% above regular panels.
Guidelines for Maximum Efficiency
Optimize mounting height and tilt by raising panels (≈1-1.5 m) for improved rear-side exposure.
Use Light-colored gravel, white paint (or) sand will improve reflected light.
Single-axis trackers or elevated fixed-tilt frames enhance back-side capture.
Keep clean spacing between rows & avoid obstructions.
Optimize the inverter settings by slightly oversizing it to accommodate greater bifacial gain.
Advantages of Bifacial Solar Panels
Higher energy yield (+5-30% production)
Lower levelized cost of energy (LCOE).
Durable glass-glass structure.
Excellent performance in snowy (or) cold conditions.
Longer longevity & slower deterioration.
Disadvantages of Bifacial Solar Panels
Higher upfront costs
Heavier than monofacial modules.
Complex installation & racking
The output varies with the ground reflectivity.
Need regular cleaning (both sides)
Applications of Bifacial Solar Panels
Utility-scale solar farms.
Commercial rooftops with reflecting surfaces.
Desert installations (high sunshine and albedo).
Snow-prone areas (rear reflection enhancement).
Building-integrated photovoltaic systems (BIPV).
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.