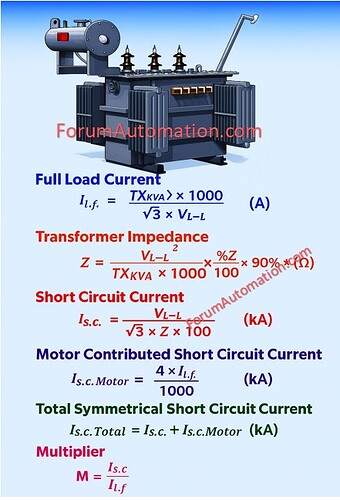
Transformer Short Circuit Calculation: Full Load, Impedance & Motor Contribution
CALCULATOR
* Transformer Short Circuit Current Calculation
1). Full Load Current
The current generated by an electrical device (such as a motor or transformer) when functioning at full capacity.
IF.L. = TXkVA × 1000√3 × VL−L (A)
2). Transformer Impedance
The internal resistance provided by a transformer to the flow of electrical power, which restricts short circuit current.
Z = VL−L2TXkVA × 1000 × %Z100 × 90% (Ω)
3). Short Circuit Current
The extremely high current that flows when a fault forms as a result of a direct connection between phases (or) phase-earth.
IS.C. = VL−L√3 × Z × 1000 (kA)
4). Motor Contributed Short Circuit Current
Running motors supply greater fault current during a short circuit because of the mechanical energy they store.
IS.C.Motor = 4 × IF.L.1000 (kA)
5). Total Symmetrical Short Circuit Current
The overall fault current at a given point in the system including contributions from transformers, generators & motors providing the waveform is balanced.
IS.C.Total = IS.C. + IS.C.Motor (kA)
6). Multiplier
A factor used to alter or scale current values while calculating, coordinating, or establishing protection devices.
M = IS.C. /IF.L
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.