Reed Switch
Relay
- A relay is an electrical switch that uses an electromagnet to turn it on or off. It is made up of a wire coil that, when powered up, creates a magnetic field that pulls a moving armature.
- The contacts that this armature is attached to can be utilized to regulate the flow of current in an electrical circuit.
- Relays are frequently employed in a variety of applications, such as home automation, automobile electronics, and industrial control systems.
How does a relay works?
- The relay makes it possible for a minimal quantity of electrical current to manage substantial amounts of load current. When voltage is applied to the coil, a tiny quantity of current flows through the coil. As a result, a greater amount of current flows through the contacts, allowing the load on the electrical circuit to be controlled.
Applications of Relays
- Industrial control systems: High-power devices, such as motors, pumps, and heaters, are switched using relays in industrial control systems. These devices can be operated more simply and safely by low-power control circuits by using relays.
- Home automation: To operate lights, appliances, and other devices, home automation systems use relays. A relay can be used, for instance, to automatically turn on and off a light switch in accordance with a schedule or when motion is detected.
- Telecommunication: Telephone lines and other signals are switched in telecommunications systems using relays. These systems can handle high volumes of traffic and can be remotely controlled by the use of relays.
- Power Transmission: Relays are used in power distribution systems to regulate the flow of electricity among various system components. These systems can be automatically regulated and can react to changes in demand or other circumstances by using relays.
- Relays are used in automobile electronics to regulate a number of features, including headlights, windscreen wipers and cooling fans.
- Relays enable these tasks to be managed by low-power signals from the car’s computer, enhancing their dependability and efficiency.
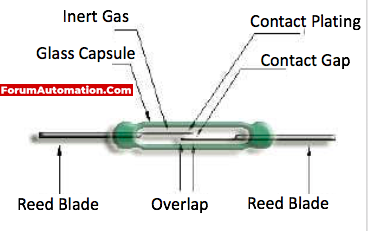
Reed Switch
-
The fundamental reed switch is made up of two identical flattened ferromagnetic reeds that are enclosed in a glass capsule with a dry inert gas to protect the contact from contamination.
-
The cantilever-shaped reeds are sealed within the capsule such that their free ends overlap and are separated from one another by a little air space.

How does Reed Switch works?
- The reeds transform into flux carriers in the magnetic circuit when a magnetic force is produced parallel to the reed switch.
- The overlapping reed ends form opposing magnetic poles that pull together. Reeds will be brought together if the magnetic force between the poles is strong enough to outweigh their own restoring force.
Applications for reed switches
-
Security systems: To track the opening and closing of doors and windows, reed switches are frequently employed in security systems. The magnetic field surrounding the reed switch is disturbed when a door or window is opened, which causes the switch to open and set off an alert.
-
Proximity Sensor: Reed switches can be used as proximity sensors to find magnetic objects, like moving parts of a machine, in close proximity. The reed switch is activated and a reaction is triggered when the magnetic object approaches it from a specific distance.
-
Medical equipment: Reed switches are used in defibrillators and blood pressure monitors to determine whether a magnetic field is there or not. The equipment’s many functionalities are triggered by this data.
-
Automotive electronics: To determine the location of a moving component, such as the crankshaft of a car, reed switches are utilized. The moving component disturbs the magnetic field surrounding the reed switch, which causes the car’s computer to react.
-
Energy meters: To detect the flow of power, reed switches are employed in energy metes. The meter’s reed switch detects the magnetic field that is produced as electricity flows through it, enabling it to calculate the amount of energy being consumed.