Real power, Reactive power and Apparent power in Electrical System
Real power, Reactive power and Apparent power in Electrical System
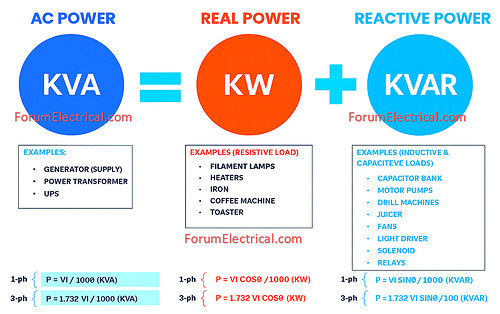
In an AC electrical system, power is not just one quantity. It’s divided into
- Real Power,
- Reactive Power and
- Apparent Power
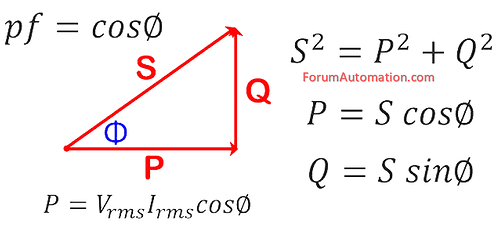
which are related to each other through the power triangle.
1). Real Power (Active Power, P)
Definition
The actual power that does useful work, like running motors, lighting lamps, heating, etc.
Unit
Watt (W) or kilowatt (kW)
Formula
P = VI cosØ
2). Reactive Power (Q)
Definition
The power that oscillates back and forth between the source and reactive components (inductors, capacitors). It does not do useful work, but it’s necessary to maintain magnetic/electric fields.
Unit
VAR (Volt-Ampere Reactive) or kVAR
3). Apparent Power (S)
Definition
The vector sum of Real and Reactive Power. It’s the total power supplied by the source.
Unit
VA (Volt-Ampere) or kVA
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.