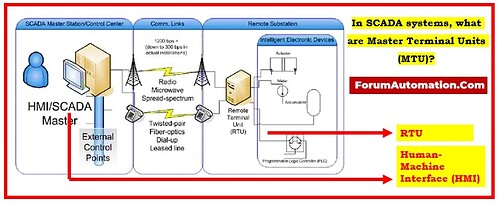
Master Terminal Units (MTUs) are not a standard or widely used term in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems. An outline of the common components present in a SCADA system are explained.
Master terminal units (MTUs) in SCADA systems send commands to Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) located away from the control, gather data, store it, process it, and display it in an array of pictures, curves, and tables to facilitate control decisions. The control center MTU operates this way.
The MTU & RTU communicate bidirectionally, but the RTU cannot start the communication. It just collects and stores field data. MTU programs initiate communication with RTUs, either manually or automatically. MTU’s automatically send 99% of RTU commands and communications. RTU sends MTU requested information. MTU is master & RTU is slave. MTU sends data to operator interface printers and CRTs via protocols. Peer-to-peer communication will replace master-slave communication between MTUs & RTUs. Thus, SCADA system MTU is its heart.
Typical SCADA systems typically include the following elements:
1). Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
2). Programmable logic controllers (PLCs)
3). Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
4). SCADA Server
5). Infrastructure for communication
1). Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
These are the field devices in charge of interacting with the field’s sensors and actuators. RTUs collect data from numerous sensors and transmit it to the SCADA system in the center for monitoring and management. They can also get instructions through the SCADA system on how to operate the field devices that are linked.
2). Programmable logic controllers (PLCs)
Another class of field device found in SCADA systems are PLCs. Particularly they are in charge of managing particular machinery or procedures. PLCs have the ability to connect with the main SCADA system, enabling centralized monitoring and management of several PLCs distributed throughout a structure or an industrial process.
3). Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
The SCADA system’s user interface is made up of the HMI. It gives operators and engineers a visual representation of the processes, real-time data, alarms, and other important information. The HMI allows for system interaction, command issuance, and process monitoring by operators.
4). SCADA Server
This is the primary element of the SCADA system in charge of managing, storing, and processing data. RTU and PLC data are gathered, processed, and then presented to the HMI for viewing. The SCADA server also executes control logic and conducts alarming and historical data logging tasks.
5). Infrastructure for communication
All the parts of the SCADA system are connected through the communication infrastructure. It provides efficient and safe data transfer between RTU’s, PLC’s, the SCADA server, and the HMI. There are several ways to communicate, including wireless protocols or physical connections (Ethernet, serial communication).
The concept of “Master Terminal Units” could refer to a particular implementation, a specialist part utilized in particular industries, or a SCADA system with particular needs.