If you don’t have any measurement instruments or labeling, you can still tell if a motor is AC or DC by carefully inspecting its construction, wiring & operational clues:
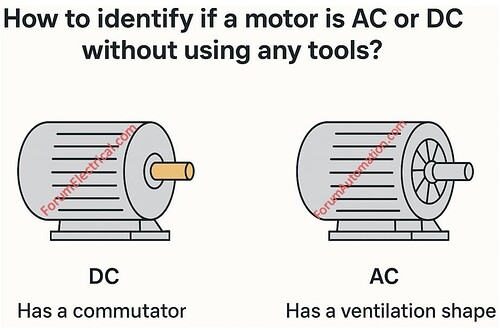
Analyze the Physical Appearance of Motor
AC Motor: Generally larger in size for same power rating, with ventilation slots and a solid, smooth stator housing.
DC Motor: May have a more compact design with a visible brush housing (or) brush caps on the body.
Look for Brushes & Commutators
AC Induction Motor: No brushes (or) commutator. The rotor is smooth and features squirrel cage bars within.
DC Motor: The motor has exposed brushes and a commutator. These are used to change the current direction in the armature.
Check the Wiring Type
AC Motor: AC Motors often have thicker stator winding leads, with either three or two wires (three-phase or single-phase).
DC Motor: A DC motor typically has two main terminals for the armature and two smaller ones for the field windings (in independently excited variants).
Rotation Behavior
AC Motor: Increases speed more gradually owing to slip.
DC Motor: Starts instantly and accelerates quickly, even under load.
Nameplates (or) Markings (If Available)
Even without tools, the casing may include etched voltage/frequency markings
AC Motor: 220V, 50Hz
DC Motor: 220V DC
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.