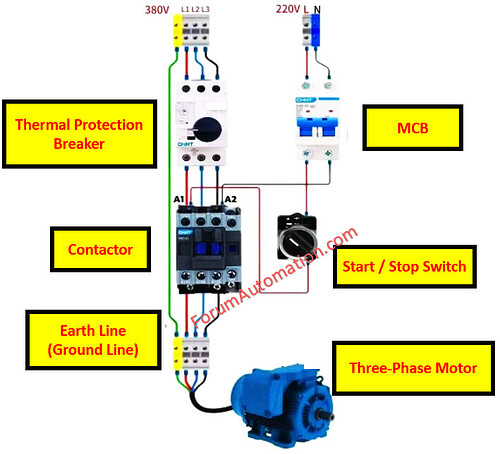
How does a Three-Phase Motor Control Circuit Work?
A three-phase motor circuit consists of two major components:
- Power circuit (380 V) &
- Control circuit (220 V).
The power circuit comprises
- Circuit breaker,
- Thermal overload relay,
- Contactor &
- Motor
which supplies and protects the motor.
The control circuit manages the start/stop operation with an MCB and an On/Off switch, safely energizing the contactor coil.
This configuration enables a low-voltage control circuit to reliably operate a high-voltage motor, providing both protection and efficiency.
Circuit Breaker (Power Circuit – 380V)
The circuit breaker (380V) protects the motor from short circuits & overcurrent failures.
Thermal Overload Relay
Prevents motor overheating by cutting power during overload conditions.
Contactor
An electromagnetic switch that operates the motor remotely via the control circuit.
3-Phase Motor
The primary load that transforms electrical energy to mechanical motion.
MCB (Control Circuit - 220V)
MCB (Control Circuit - 220V) protects the control circuit from short circuits (or) malfunctions.
Start-Stop Switch
Manually control the contactor coil to start or stop the motor.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.