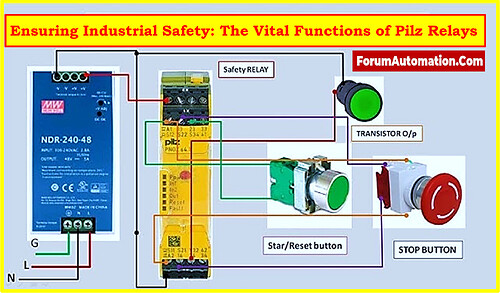
What is a Pilz relay?
- A Pilz relay, commonly referred to as a Pilz safety relay, is an essential part of systems for industrial automation and machinery safety.
- These relays are created by Pilz, a reputable producer of safety automation devices, to guarantee the safe operation of machinery and safeguard both employees and equipment from injury.
- In the framework of safety automation, Pilz relays perform a number of crucial tasks.
What is the purpose of a safety relay?
Safety Monitoring:
- The main function of Pilz relays is safety monitoring.
- They continuously evaluate the state of several safety-related conditions and inputs in a manufacturing environment.
- These inputs can include safety sensors, safety gates, emergency stop buttons, and more.
- Pilz relays are critical in maintaining a safe working atmosphere by monitoring these inputs.
Emergency Stop Function:
- The emergency stop (E-stop) function is one of the Pilz relay’s most important roles.
- The relay quickly cuts off the electricity to the machinery in the event of an emergency, such as a worker in distress or a dangerous condition discovered by a safety sensor.
- This immediate shutdown can save accidents from happening and safeguard people from damage.
Safety Interlocking:
- For machinery or production processes, Pilz relays are employed to regulate access to dangerous areas.
- For instance, before allowing the machine to work, they can make sure that a safety gate is tightly closed.
- This interlocking system aids in preventing unsafe or unauthorized access to risky areas.
Monitoring Safety Sensors:
- Industrial environments frequently use safety sensors including light curtains, safety mats, and safety switches.
- Pilz relays are made to continuously check the status of these sensors.
- The relay can start a safety response, such as stopping the machine or raising an alarm, if a sensor detects a safety breach, such as an object or person entering a restricted area.
Guarding and Perimeter Protection:
- Pilz relays are essential for perimeter safety and protection. They can keep an eye on barriers, fencing, or safety measures.
- The relay can immediately respond to stop the machinery in the event that a guard is removed, tampered with, or if an unauthorized entrance attempt is made. This prevents accidents and injuries.
Handling Multiple Inputs:
- These relays may simultaneously process several inputs from different safety devices.
- They assess the inputs and determine whether it is safe to let the machine run normally or whether an emergency stop is necessary.
- Due to their adaptability, they can be used in manufacturing environments with a variety of sophisticated safety needs.
Fault Tolerance:
- Redundancy and self-monitoring characteristics are included into Pilz relays.
- The relay can make adjustments to preserve safety if a part inside it malfunctions or a fault is found.
- This guarantees that the level of safety will not be compromised even in the event that there is a malfunction.
Reset and Restart Functions:
- Pilz relays can perform reset and restart operations following the resolution of an emergency stop condition.
- These features allow for the safe restart of machine operations, avoiding unanticipated restarts that may harm employees.
Safe Control of Robots:
- Pilz relays can be used in robotics applications to regulate the robots’ safe operation.
- This guarantees that robots operate within established safety limitations and do not endanger adjacent workers.
Summary:
- Pilz relays are integral components of industrial safety systems, helping industries comply with safety standards and regulations while safeguarding workers and equipment.
- Their multifaceted functions, including emergency stop capabilities, safety interlocking, sensor monitoring, guarding, fault tolerance, and more, contribute to the prevention of accidents and the promotion of workplace safety.
- Implementing Pilz relays in industrial settings not only protects personnel but also helps maintain the integrity and reliability of industrial processes.
- Adherence to relevant safety standards and guidelines is essential when integrating Pilz relays to ensure the highest level of safety in industrial automation.