The type of voltage employed in a megger test (insulation resistance test) is determined by the insulation system and equipment under test.
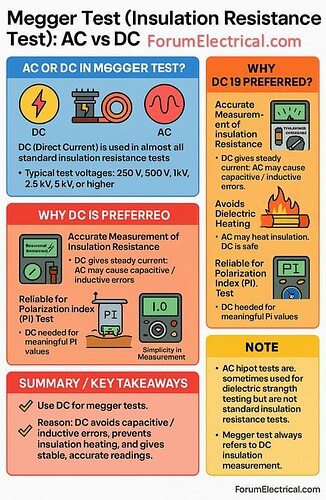
Megger Test: AC or DC?
Almost all conventional insulation resistance tests use direct current (DC).
Typical test voltages include 250 V, 500 V, 1 kV, 2.5 kV, 5 kV and higher depending on the equipment’s rating.
AC (Alternating Current) is rarely utilized for insulation resistance testing since DC provides more precise and reliable results.
Why DC is Preferred?
Insulation resistance can be measured accurately.
DC generates a constant current allowing the megger to measure insulating resistance without interference from reactances.
AC can produce capacitive & inductive effects, resulting in inaccurate low readings.
Avoids dielectric heating.
High alternating current voltage may heat the insulation because of dielectric losses, potentially harming it.
DC provides a constant voltage without generating substantial heat.
Polarization Index (PI) Test
PI testing which assesses insulation quality over time requires DC. AC cannot generate a valid PI value.
Simplicity of Measurement
The majority of insulation testers (meggers) are built for DC measurement and include internal DC generators (or) batteries.
AC hipot (high-potential) tests are occasionally used for extremely high-voltage equipment, however they are a dielectric strength test rather than a typical insulation resistance test.
Megger tests are always used to determine DC insulation resistance.
Megger testing should be performed using direct current.
DC eliminates capacitive or inductive mistakes inhibits insulation heating, and provides consistent accurate insulation resistance readings.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.