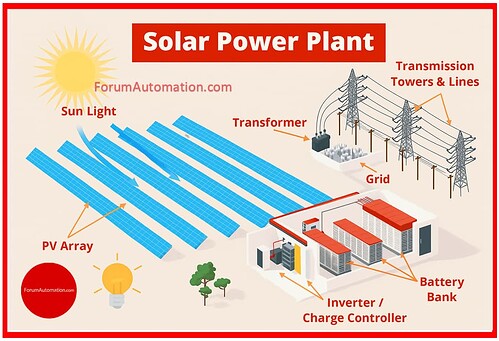
Yes, solar power plants have an impact on the transmission network, positively as well as negatively, based on their size, location & level of integration.
Positive Effects
Reduced Transmission Losses
When solar plants are built near load centers (such as rooftop solar (or) local solar farms), electricity travels shorter distances, resulting in lower transmission and distribution (T&D) losses.
Peak Load Support
Solar power frequently corresponds with daytime peak demand (air conditioning, industrial loads), decreasing the strain on transmission lines and substations.
Deferred Infrastructure Upgrades
If solar output offsets demand growth, new transmission lines or modifications may not be required.
Negative or Challenging Effects
Intermittency and Variability
Solar output varies with the weather & time of day. This inconsistency creates voltage variations, necessitating a rapid balance between generation and demand on the transmission network.
Reverse Power Flow
In locations with high solar penetration, excess generation can flow back into the grid, putting strain on transformers, protection devices and transmission equipment that were not meant for bidirectional flow in the first place.
Grid Stability Issues
Frequency Stability
A sudden decline in solar output (cloud cover) may result in frequency variations.
Voltage Regulation
In weak grids, high solar injection can lead to overvoltage.
Inertia Reduction
Unlike synchronous generators, solar inverters lack inherent inertia, making the grid more susceptible to shocks.
Transmission Congestion
Large-scale solar plants are frequently found in remote sunny places (deserts, rural areas) far from population centers. This may cause congestion in transmission routes unless new lines are built.
Protection Coordination
Traditional protection solutions presume unidirectional power flow. With solar integration, relay settings & fault current contributions may need to be adjusted.
Solutions & Mitigation
Batteries help to smooth out solar variations and reduce load on the transmission network.
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS)
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) enhance voltage and power flow management.
Smart Grid Technologies
Smart Grid technologies include improved monitoring, real-time balancing & adaptive protection.
Hybrid Systems
Solar, wind & conventional plants lessen dependency on a single intermittent source.
Upgraded Transmission Lines
Creating HVDC or high-capacity AC lines connecting solar-rich regions to demand centers.
Well-integrated solar power plants can improve grid dependability and reduce losses, but they also face obstacles such as variability, reverse power flow & instability. Proper grid planning, smart technology, and storage solutions are required to ensure the safe and efficient integration of solar electricity into the transmission system.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.