What is Linear Load?
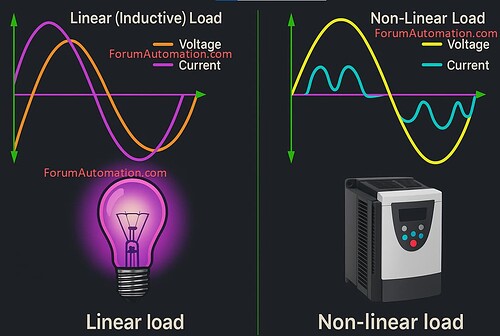
Linear loads in electrical systems are devices (or) equipment that draw current in a sinusoidal way proportional to the applied voltage.
These loads have a linear voltage-current relationship resulting in a stable power factor and minimum waveform distortion.
Eg: Linear loads include resistive heaters, incandescent lamps and induction motors that are fully loaded.
What is Non-Linear Load?
Non-linear loads are electrical devices or equipment that produce non-sinusoidal current waveforms whenever connected to an alternating current power source.
Non-linear loads distort voltage and current waveforms due to internal circuitry, while linear loads pull current in a smooth sinusoidal pattern.
These devices introduce harmonics into the electrical system causing power quality issues like as voltage distortion and increased losses in wires and transformers.
Eg: Common examples include computers, LED illumination, variable speed drives, and switching power sources.
Difference between Linear and Non-Linear Loads
Linear vs Non-Linear Loads
| Parameter | Linear Load | Non-Linear Load |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A load in which the current waveform follows (is proportional to) the applied voltage waveform. | A load in which the current waveform does not follow the voltage waveform; current is distorted. |
| Waveform Shape | Pure sine wave (same shape as supply voltage). | Distorted, non-sinusoidal waveform (contains harmonics). |
| Current–Voltage Relationship | Linear load follows Ohm’s Law (V = IR) at all times. | Non-linear load does not follow Ohm’s Law due to varying impedance. |
| Harmonic Generation | No harmonics generated. | Produces harmonics that can distort the power system. |
| Power Factor | Near unity (high power factor). | Poor or distorted power factor due to harmonics. |
| Examples | Incandescent lamps, resistive heaters, electric iron, simple motors, fans. | Computers, LED drivers, UPS, variable frequency drives (VFDs), SMPS, fluorescent lights. |
| Effect on System | Stable voltage and current, no waveform distortion. | Causes voltage distortion, overheating in cables/transformers, and reduced equipment life. |
| Measurement Tools | Normal voltmeter and ammeter sufficient. | Requires True RMS meters or power analyzers for accurate readings. |
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.