Difference between ACB and VCB
The difference between ACB and VCB are:
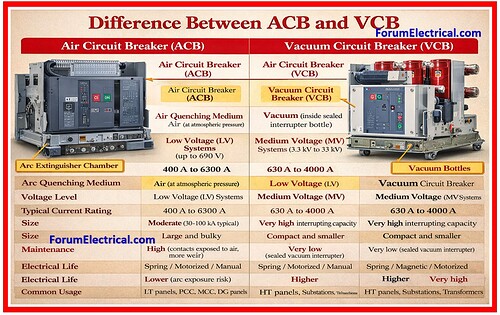
| Feature | ACB (Air Circuit Breaker) | VCB (Vacuum Circuit Breaker) |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | Air Circuit Breaker | Vacuum Circuit Breaker |
| Arc quenching medium | Air (at atmospheric pressure) | Vacuum (inside sealed interrupter bottle) |
| Voltage level | Used mainly in Low Voltage (LV) systems (up to 690 V) | Used in Medium Voltage (MV) systems (3.3 kV to 33 kV) |
| Typical current rating | 400 A to 6300 A | 630 A to 4000 A |
| Breaking capacity | Moderate (50–100 kA typical) | Very high interrupting capacity |
| Size | Large and bulky | Compact and smaller |
| Maintenance | High (contacts exposed to air, more wear) | Very low (sealed vacuum interrupter) |
| Contact erosion | Higher due to arc in air | Very minimal due to arc extinction in vacuum |
| Operating mechanism | Spring / motorized / manual | Spring / magnetic / motorized |
| Electrical life | Lower | Higher |
| Mechanical life | Moderate | Very high |
| Safety | Lower compared to VCB (arc exposure risk) | Higher (arc contained inside vacuum bottle) |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but economical long-term |
| Typical applications | LT panels, PCC, MCC, DG panels | HT panels, substations, transformers, motors |
| Insulation medium | Air | Vacuum bottle + air/epoxy insulation |
| Switching frequency | Moderate | Suitable for frequent switching |
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.