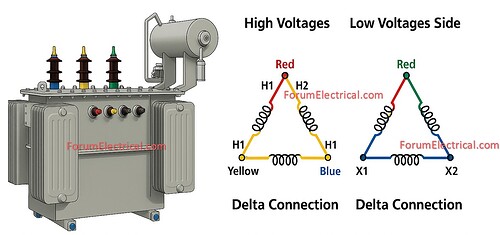
Delta-Delta (Δ-Δ) Configuration in Transformers
In a Delta-Delta transformer connection both primary and secondary windings are linked in Delta (Δ) mode.
Each phase winding is connected end-to-end resulting in a closed triangular loop that allows line voltage to equal phase voltage.
Characteristics of Delta-Delta (Δ-Δ) Transformer
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Winding connection | Primary: Δ and Secondary: Δ |
| Phase shift | No phase shift (0°) between primary & secondary |
| Line Voltage | Equal to Phase Voltage |
| Neutral availability | No neutral point |
| Harmonics | Circulates triplen harmonics within delta → good for harmonic suppression |
Advantages of Delta-Delta (Δ-Δ) Transformer
- Suitable for unbalanced loads
- No neutral required
- Ideal for 3-phase loads only
- Transformer may operate temporarily regardless if one winding fails (open-delta or V-V operation)
- Prevents third harmonics from entering system
- Improvees power quality
- Lower insulation requirements (each phase connected line-to-line)
Disadvantages of Delta-Delta (Δ-Δ) Transformer
- Single-phase loads require a neutral configuration.
- Not appropriate for neutral grounding.
- Increased short-circuit current compared to other designs.
- Difficult fault identification under specific conditions (circulating currents).
Application of Delta-Delta (Δ-Δ) Transformer
- Industrial distribution systems
- Large 3-phase motor loads
- Short-distance transmission
- Open-delta (V-V) backup operation in substations
- Step-down/step-up across two balanced 3-phase networks without the need for neutral.
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.