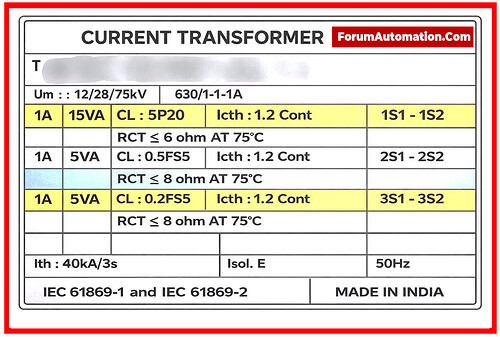
CT NAMEPLATE PARAMETERS
1). Rated Primary Current (Ip)
Example:
• 400 A
• 800/400/200 A (multi-ratio)
2). Rated Secondary Current (Is)
• 5A (most common for LV/MV panels)
• 1A (long cable runs, reduces burden losses)
3). CT Ratio
Example:
• 400/5
• 800/1
If multi-ratio:
• 800-400-200/1
4). Burden (VA)
Example:
• 5 VA
• 10 VA
• 15 VA
• 30 VA
This means the CT can supply that many volt-amperes without exceeding accuracy limits.
5). Accuracy Class
Examples:
• Metering: 0.2, 0.5, 1.0
• Protection: 5P10, 5P20, 10P10
• Special: PX, PR
6). Frequency
• 50 Hz (India)
• 60 Hz (US)
7). Insulation Level
Example for 11 kV CT:
• 12/28/75 kV
Meaning
• 12 kV → rms working
• 28 kV → 1-min power-frequency withstand
• 75 kV → lightning impulse withstand
8). Thermal Short-Time Current (Ith)
CT must survive short-circuit for 1 second.
Example:
• 25 kA, 1 sec
• 31.5 kA, 1 sec
9). Dynamic Current (Idyn)
Withstand peak current (electrodynamic forces).
Typically:
I_dyn = 2.5 x I_th
Example:
If Ith = 25 kA → Idyn ≈ 62.5 kA
10). Knee Point Voltage (Vk) (ONLY for PX class)
Example:
• Vk ≥ 120 V
• Vk ≥ 150 V
Important for differential relay operation.
11). Magnetizing Current (Im)
Typical:
• ≤ 30 mA at Vk/2
12). Secondary Winding Resistance (Rct)
Given in ohms.
Used for checking:
• Volt-drop
• CT saturation
• Relay burden calculation
13). Polarity Marking (P1, P2, S1, S2)
Important for CT orientation.
• P1 → Towards the source
• P2 → Towards the load
• S1 → Relay/meter positive
• S2 → Common/neutral
14). CT Type
• Wound type
• Bar type
• Ring type (core type)
15). Thermal Rating Factor (TRF)
Example:
• 1.2 times continuous current
Means CT can carry 20% overload continuously.
16). Standards (IS/IEC)
• IEC 61869-2
• IS 16227-2 1. Rated Primary Current (Ip)