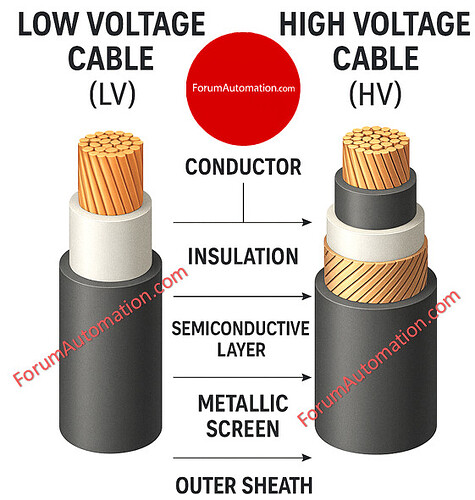
Comparison Between Low Voltage (LV) and High Voltage (HV) Power Cables
Low Voltage (LV) vs High Voltage (HV) Power Cables
| Parameters | Low Voltage (LV) Cable | High Voltage (HV) Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Range | Up to 1 kV (Typically 230V–1000V) | Above 33 kV (often 66 kV, 132 kV, 220 kV, 400 kV) |
| Application | Domestic wiring, small industries, internal plant distribution | Power transmission over long distances, substations, grid connections |
| Insulation Type | PVC, XLPE (simple layers) | XLPE, EPR with multiple insulation and shielding layers |
| Construction | Simple – Conductor, Insulation, Outer Sheath | Complex – Conductor, Semi-conductive layers, Insulation, Metallic screen, Outer sheath |
| Armouring | Usually steel wire armoured for mechanical protection | Not always used; instead, has metallic screen for electric field control |
| Testing Requirements | Basic insulation resistance and continuity tests | Partial discharge, impulse testing, HV withstand, and sheath integrity tests |
| Size/Weight | Smaller diameter, lighter weight | Larger diameter, heavier due to insulation and shielding |
| Installation | Easier to install and bend | Requires careful handling and trained personnel |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to material and construction complexity |
| Safety Precautions | Standard PPE and safety procedures | High-level PPE, insulation monitoring, safety grounding necessary |
You can also follow us on AutomationForum.co, Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Instrumentation updates.
You can also follow us on ForumElectrical.com , Facebook and Linkedin to receive daily Electrical updates.